Diabetic Foot
A diabetic foot is any pathology that results directly from Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) and / or sensory neuropathy affecting the feet in diabetes mellitus; it is a long-term complication of Diabetes Mellitus.
Book Appointment
Signs of Diabetic foot:
- Changes in skin colour
- Changes in skin temperature
- Swelling in the foot / ankle
- Pain in the legs
- Open sores on the feet that are slow to heal or are draining
- Ingrown toe nails or toe nails infected with fungus
- Corns or calluses
- Dry cracks in the skin, especially around the heel.
- Diminished ability to sense hot and cold.
- Discharge with foul odour
Causes of Diabetic foot:
- Poorly fitted or poor quality shoes.
- Poor hygiene (not washing regularly or thoroughly or not drying the feet well after washing)
- Uncontrolled blood sugar : directly affects the nerves of the leg.
- Uncontrolled blood sugar : damages the blood supply of the leg.
- Uncontrolled blood sugar : makes the muscle and the skin weak.



Diagnosis :
Whom should you consult
- Check on symptoms
- Blood sugar tests – FBS, PPBS, HbA1c
- General physician / Endocrinologist/ Diabetologist for blood sugar control and whole body evaluation
- Neurologist for assessment of Nerve assessment
- Plastic Surgeon /Diabetic foot expert for wounds in the foot
Complications
- foot ulcers or wounds that do not heal
- infections, including skin infections,bone infections, and abscesses
- gangrene, when an infection causes tissue death
- foot deformity
- Charcot’s foot, which alters the shape of the feet as bones in the foot and toe shift or break leading to permanent physical changes.
- Amputation in case of gangrene.
Treatment
Blood Sugar control : Controlling blood sugar prevents the progression of diabetic foot. Medical treatment with good blood sugar control, antibiotics required to prevent infections and medications to improve blood supply, go a long way to protect your foot.
Wound dressings offer protection and barrier to external contaminants while promoting absorption of discharges around the ulcer. Different types of dressings are available to promote wound healing. Negative pressure wound therapy : This involves removal of wound fluid through a sealed vacuum. This is aimed at improving tissue perfusion and promotion of granulation tissue.
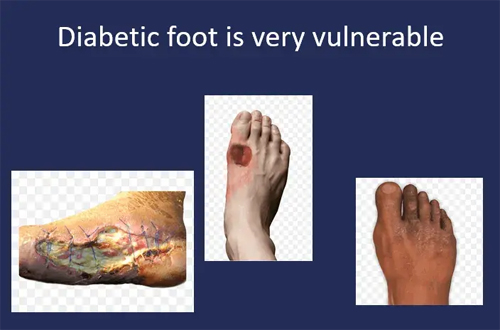
Debridement Surgery
- Getting rid of dead debris and necrotic tissues
- It forms the main stay of treatment
- Has to be aggressive because the infection spreads inside
- Many sittings of debridement may be required
- At the end the wound becomes clean and reddish
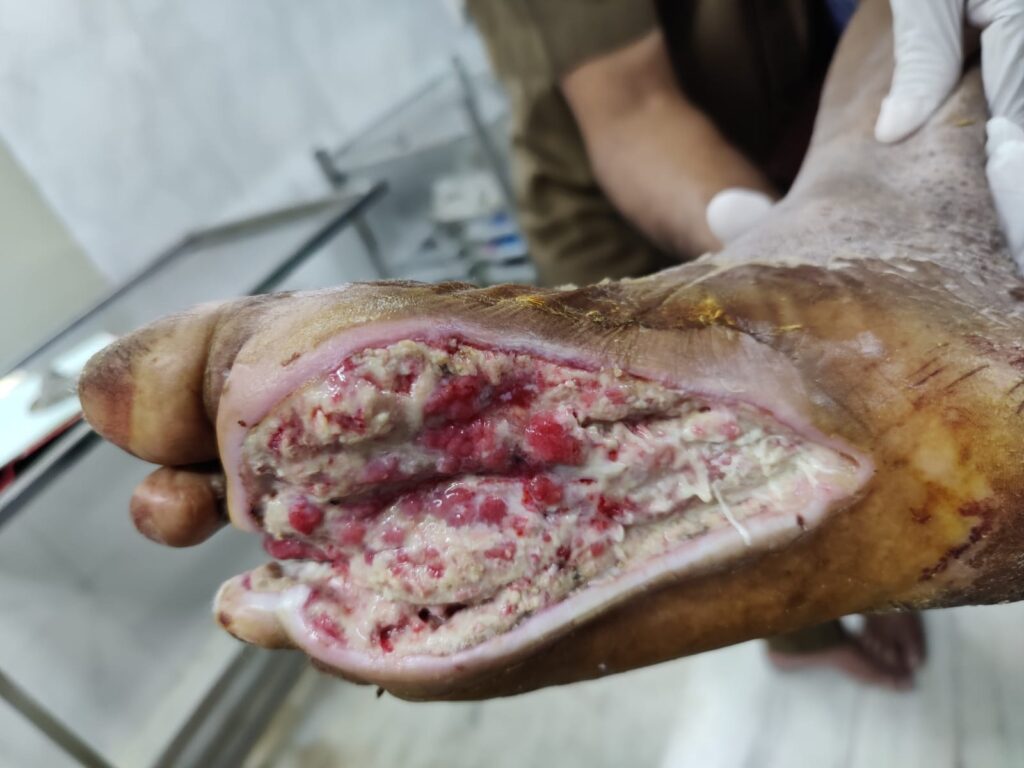
Reconstructive Surgery
- Simple stitching
- Skin grafting
- Local flaps from nearby areas
- Flaps from other areas
- Nerve release to increase sensation and healing
Growth factors and skin substitutes
Bio-physiological stimulants of wound healing like growth factors including platelet-derived growth factors, epidermal growth factors, etc also form a major role in speeding up the wound healing process.
Skin Grafting
Foot Care



Foot Wear

