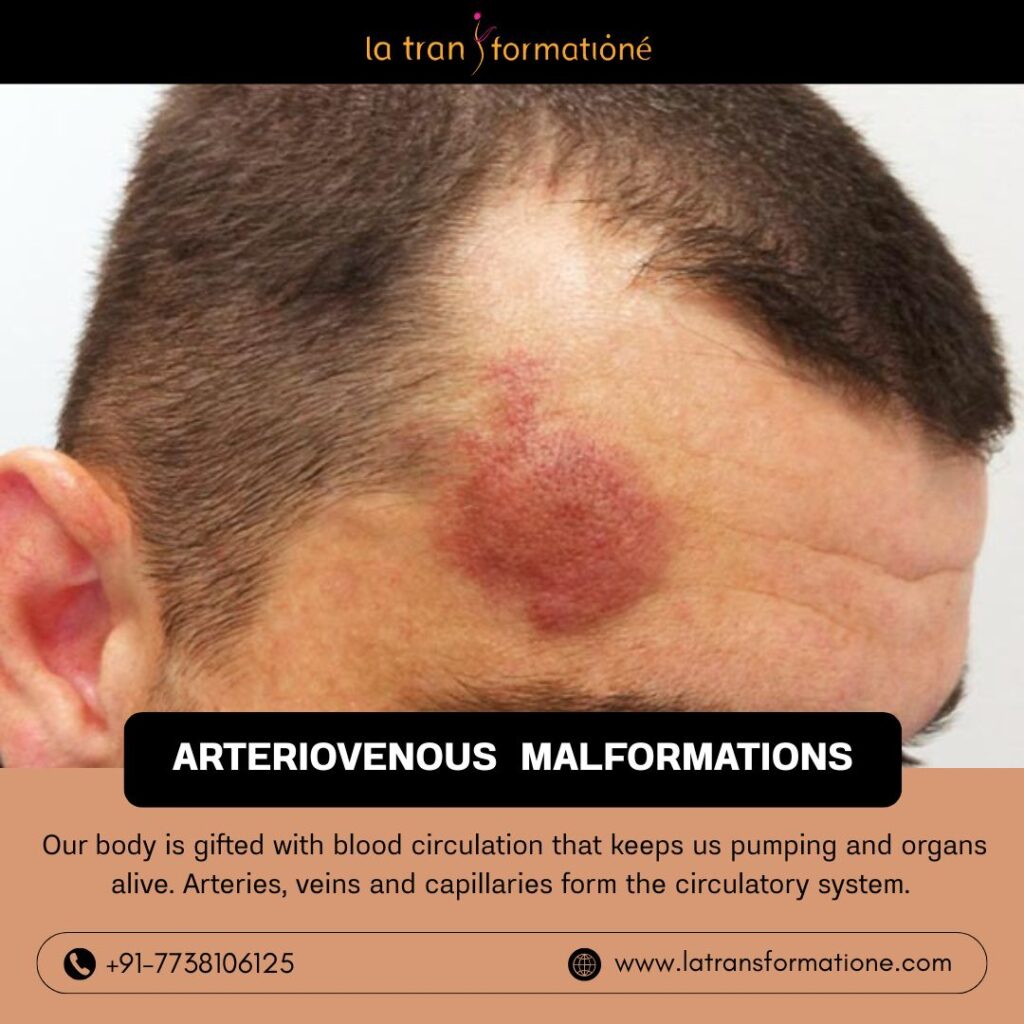
ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
Our body is gifted with blood circulation that keeps us pumping and organs alive. Arteries, veins and capillaries form the circulatory system. Arteries carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the body and veins bring back deoxygenated blood from the body to the heart. Between these, capillaries act as bridge.
In some individuals, there is an abnormal tangle and connection between arteries and veins without the supporting capillaries known as Arteriovenous malformation. Because of this shortcut, blood flows too fast and unevenly which can cause concerns. These are usually congenital (since birth).
Where can they occur?
- Brain
- Spinal cord
- Face, arms or legs
Why do you need to be watchful?
- The abnormal vessels can become weak at some point, burst and cause bleeding.
- If it occurs in the brain, it can lead to headache, stroke or seizures (fits)
- If it occurs on the skin or face, it will appear like a reddish swelling or patch or lump that grows with time which can impair function and appearance.
What should I look out for?
- Pulsating skin or reddish patch on skin
- Unexplained headaches or seizures
- Pain or swelling in affected area.
- Muscle weakness or numbness in one side of the body
- Dizziness or vertigo
- Nausea and vomiting
- Visual disturbances
How are Arteriovenous Malformations diagnosed?
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Cerebral Angiography
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA)
- CT scan
Can Arterio Venous Malformations be treated?
Yes, the treatment of choice varies depending on the size and location of the lesion.
Options include:
- Medications: Medications cannot cure Arteriovenous Malformations, but can manage symptoms
- Observation: If the AVM is not causing symptoms and if the chances of bleeding are low, monitoring it is an option.
- Microsurgery: Small AVM’s that are in an easy to approach location can be removed through microsurgery.
- Endovascular Embolization: A catheter is threaded through an artery to the AVM, where a glue-like substance or other material is injected to block blood flow. This is often used before surgery or radiosurgery to reduce the AVM's size and risk.
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS): This non-invasive procedure uses highly focused radiation beams to damage the AVM's blood vessels, causing them to scar and close over time. It is typically used for small AVMs that are difficult to reach surgically.
Most AVMs are congenital, meaning they are present at birth, and the exact cause is not well understood, and hence they cannot be prevented.
The outlook for people with an AVM varies widely. While some live their whole lives without symptoms, others can experience severe or fatal complications, especially from a rupture. Treatment can be highly effective, and doctors use careful assessments to determine the best approach for each individual.
If you or any one in your social circle needs solution on Arterio venous malformation, talk to us today. Reach out to us on 7738106125 and speak with our Senior Microvascular and Plastic surgeon himself and get the best.